How properly develop KERs and business plan ideas for innovative projects?

For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), identifying Key Exploitable Results (KERs) and building a robust business plan is crucial for turning innovative ideas into market success.
The next section outlines the approach adopted by FFplus WP4 to support SMEs and start-ups involved in sub-projects.
Key Exploitable Results
For SMEs, understanding KERs is crucial, as each KER represents a distinct and valuable project outcome with clear commercialisation potential. These can be things like new products or services, new ways of doing things, or their own special technologies. Or maybe it's something else, like protected intellectual property like patents or trademarks, or maybe it's their unique expertise.
In order to effectively identify the KERs, we must systematically review all project outcomes and deliverables. Next, we should assess the uniqueness of the results by identifying what distinguishes them from existing solutions. Then the potential for exploitation should be evaluated by determining how these outcomes could be used, sold or licensed. Finally, the KERs should be safeguarded by considering protection options, such as intellectual property rights.
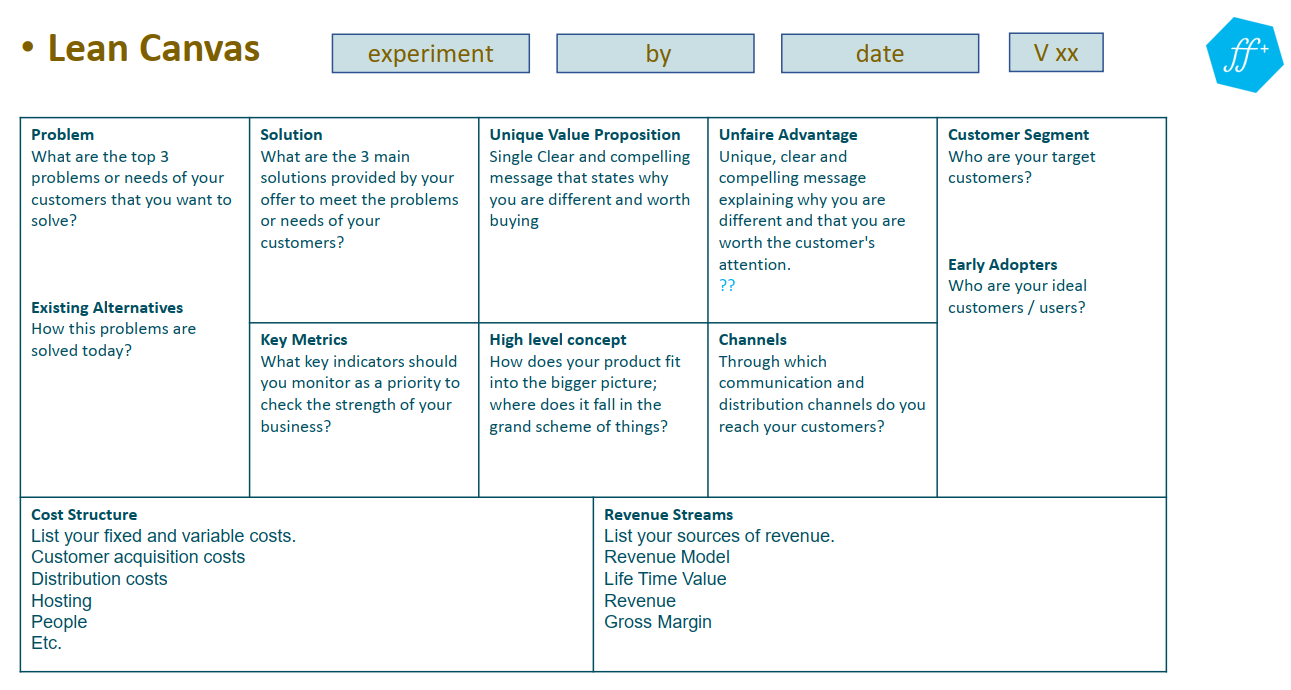
Lean Canvas
A business idea can be defined quickly using the Lean Canvas is a one-page tool that can be used to quickly define a business idea by outlining core assumptions. It helps clarify the problem that the innovation solves, the solution that it provides, its unique value proposition, and its target customer segments. It also helps to consider revenue streams and cost structure.
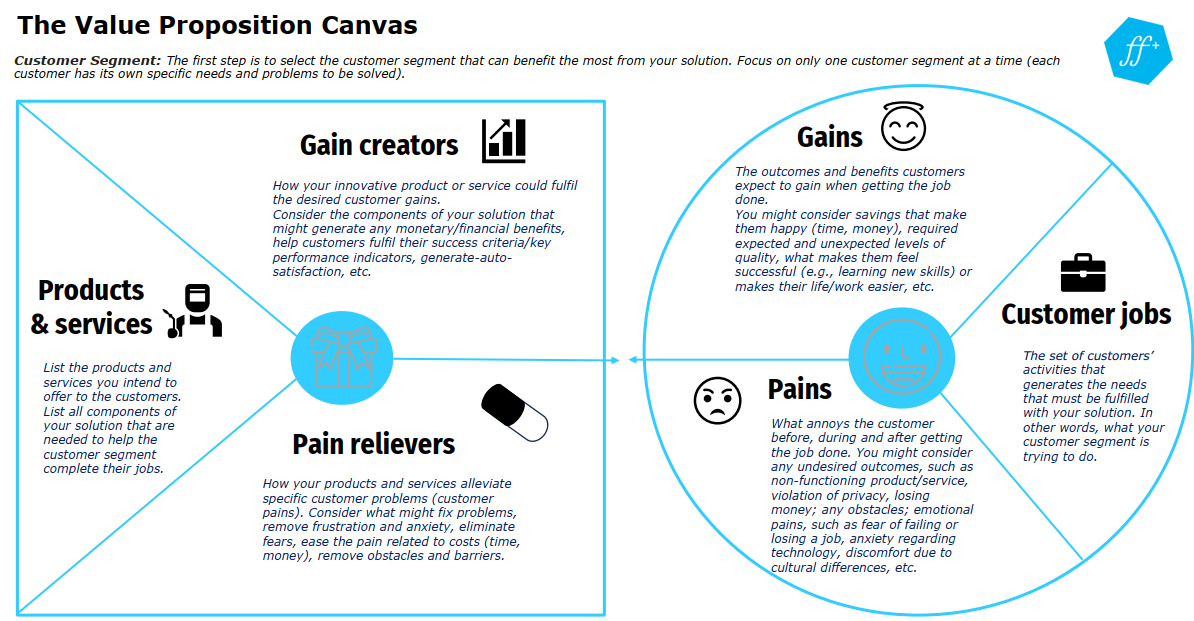
Value Proposition Canvas
The Value Proposition Canvas (VPC) is a key tool for aligning the KER with customer needs. On the Customer Side, it helps identify the jobs customers need done, their frustrations (pains), and their desired benefits (gains). Correspondingly, on the Value Proposition Side, it details how the products and services specifically act as pain relievers and gain creators for those customers.
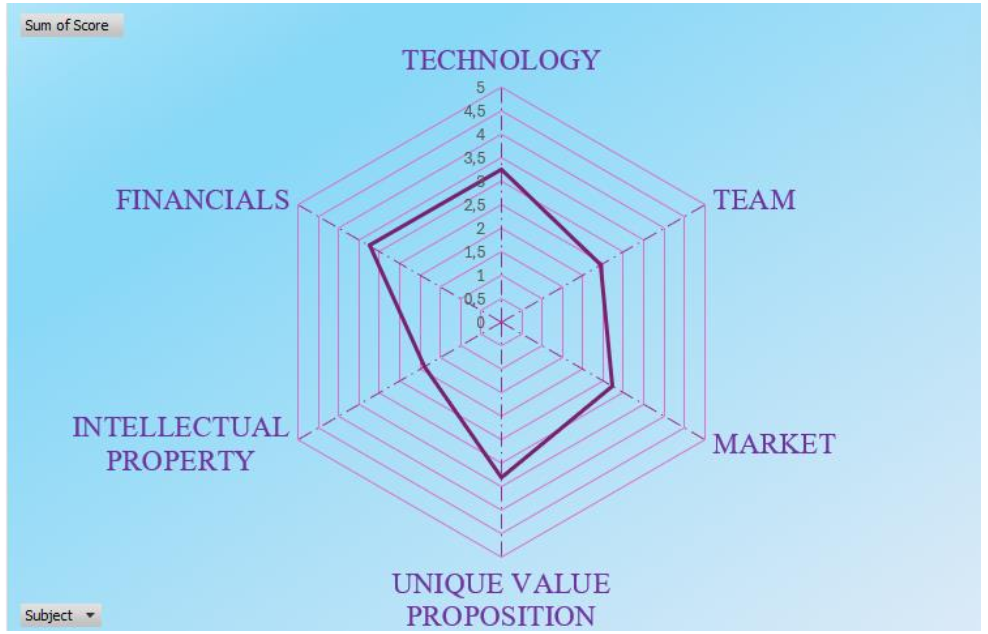
Bosat
SMEs will find the Business Opportunity Self-Assessment Tool (BOSAT) invaluable. It helps them self-assess the maturity of their business idea in key areas. It prompts them to evaluate factors such as market demand for their innovation, the robustness and market readiness of the KER, the skills of the team, and financial projections and funding needs.
Detailed Business Plan Structure
To get a full picture, SMEs business plan needs to include an Executive Summary (project overview, KERs, strategy), a Company Description (mission, vision, values), and a detailed Market Analysis (target market, trends, competitors). It should also detail their products and services, outline the marketing and sales strategy, and present an operational plan for day-to-day business functions. Finally, it should introduce the management team and provide a robust financial plan, including forecasts, funding needs and profitability.
Combining the rigorous identification of KERs with strategic planning using these tools allows innovative HPC-based projects to maximise their impact and commercial potential.
Author: Samir Been Chabane, Teratec
